I am obsessed with the “Everydays” posted by Mike Winkelmann — and I love seeing the same characters and themes crop up in different contexts (see them all on Instagram).




I am obsessed with the “Everydays” posted by Mike Winkelmann — and I love seeing the same characters and themes crop up in different contexts (see them all on Instagram).




Exercise, by W. S. Merwin, via Matthew Ogle’s Pome (also available via Poetry Foundation).
Exercise
First forget what time it is
for an hour
do it regularly every daythen forget what day of the week it is
do this regularly for a week
then forget what country you are in
and practice doing it in company
for a week
then do them together
for a week
with as few breaks as possiblefollow these by forgetting how to add
or to subtract
it makes no difference
you can change them around
after a week
both will help you later
to forget how to countforget how to count
starting with your own age
starting with how to count backward
starting with even numbers
starting with Roman numerals
starting with fractions of Roman numerals
starting with the old calendar
going on to the old alphabet
going on to the alphabet
until everything is continuous againgo on to forgetting elements
starting with water
proceeding to earth
rising in fireforget fire
Rebecca Solnit, from A Field Guide to Getting Lost.
“Of course to forget the past is to lose the sense of loss that is also memory of an absent richness and a set of clues to navigate the present by; the art is not one of forgetting but letting go. And when everything else is gone, you can be rich in loss.”
Richard Siken, via Pome by Matthew Ogle.
from The Language of the Birds
4
To be a bird, or a flock of birds doing something together, one or many, starling or murmuration. To be a man on a hill, or all the men on all the hills, or half a man shivering in the flock of himself. These are some choices.
The night sky is vast and wide.
A man had two birds in his head—not in his throat, not in his chest—and the birds would sing all day never stopping. The man thought to himself, One of these birds is not my bird. The birds agreed.
Frank Budgen, via Geoff Manaugh on “The City That Remembers Everything,” a rhyme to Borges’ 1:1 map.
One important personality that emerges out of the contacts of many people is that of the city of Dublin.
“I want,” said Joyce, as we were walking down the Universitätsträsse, “to give a picutre of Dublin so complete that if the city one day suddenly disappeared from the earth it could be reconstructed out of my book.”
From Italo Calvino’s Invisible Cities, a reminder via Jason Kottke:
“The inferno of the living is not something that will be; if there is one, it is what is already here, the inferno where we live every day, that we form by being together. There are two ways to escape suffering it. The first is easy for many: accept the inferno and become such a part of it that you can no longer see it. The second is risky and demands constant vigilance and apprehension: seek and learn to recognize who and what, in the midst of inferno, are not inferno, then make them endure, give them space.”
Adam Phillips in the Paris Review via Austin Kleon (emphasis his).
“[I]f you live in a culture which is fascinated by the myth of the artist, and the idea that the vocational artistic life is one of the best lives available, then there’s always going to be a temptation for people who are suffering to believe that to become an artist would be the solution when, in fact, it may be more of the problem. There are a number of people whom you might think of as casualties of the myth of the artist. They really should have done something else. Of course some people get lucky and find that art works for them, but for so many people it doesn’t. I think that needs to be included in the picture. Often one hears or reads accounts in which people will say, Well, he may have treated his children, wives, friends terribly, but look at the novels, the poems, the paintings. I think it’s a terrible equation. Obviously one can’t choose to be, as it were, a good parent or a good artist, but if the art legitimates cruelty, I think the art is not worth having. People should be doing everything they can to be as kind as possible and to enjoy each other’s company. Any art, any anything, that helps us do that is worth having. But if it doesn’t, it isn’t.”
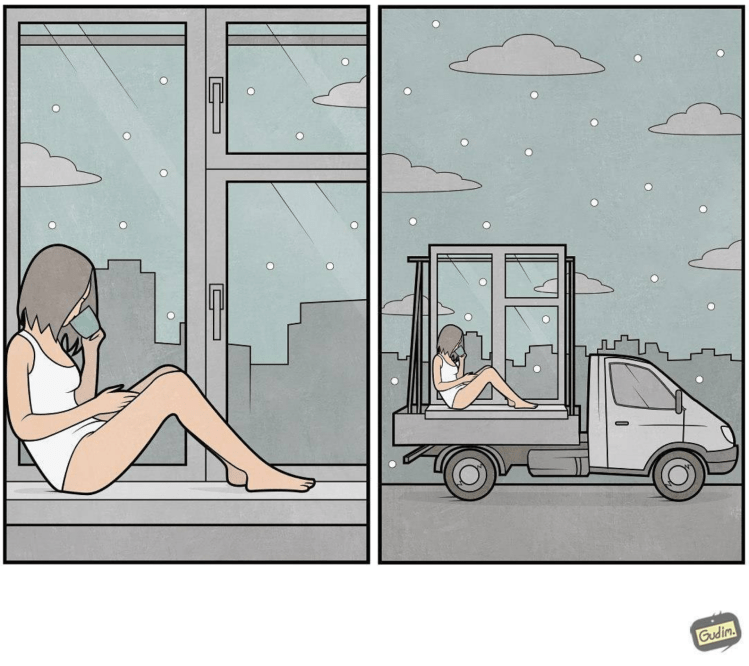
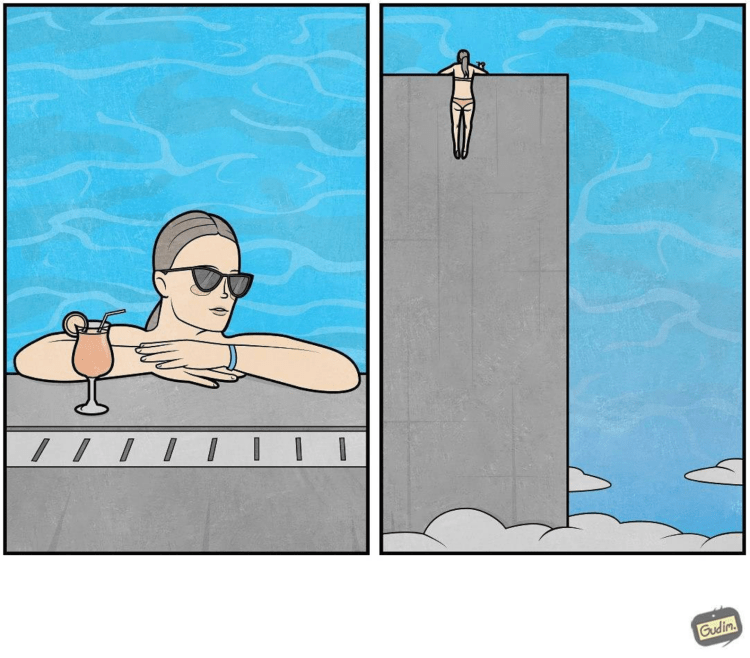
I love these clever illustrations by Gudim Anton (via Instagram).

From Henry Farrell‘s “Philip K. Dick and the Fake Humans.”
Standard utopias and standard dystopias are each perfect after their own particular fashion. We live somewhere queasier—a world in which technology is developing in ways that make it increasingly hard to distinguish human beings from artificial things. The world that the Internet and social media have created is less a system than an ecology, a proliferation of unexpected niches, and entities created and adapted to exploit them in deceptive ways. Vast commercial architectures are being colonized by quasi-autonomous parasites. Scammers have built algorithms to write fake books from scratch to sell on Amazon, compiling and modifying text from other books and online sources such as Wikipedia, to fool buyers or to take advantage of loopholes in Amazon’s compensation structure. Much of the world’s financial system is made out of bots—automated systems designed to continually probe markets for fleeting arbitrage opportunities. Less sophisticated programs plague online commerce systems such as eBay and Amazon, occasionally with extraordinary consequences, as when two warring bots bid the price of a biology book up to $23,698,655.93 (plus $3.99 shipping).
….
In his novels Dick was interested in seeing how people react when their reality starts to break down. A world in which the real commingles with the fake, so that no one can tell where the one ends and the other begins, is ripe for paranoia. The most toxic consequence of social media manipulation, whether by the Russian government or others, may have nothing to do with its success as propaganda. Instead, it is that it sows an existential distrust. People simply do not know what or who to believe anymore.
From Eugene Lim’s Dear Cyborgs.
“Childhood was hell but also paradise. In retrospect it was safe because we survived it. And so in it we were not yet destroyed or scarred or proven failures or dumb or worn-out or brokenhearted. And furthermore, the warmth of brotherhood never as cozy and pure as when the enemy surrounds…”
From Jason Mark’s Satellites in the High Country:
“When I think about wildness as a civic good, Thoreau’s famous dictum—”in wildness is the preservation of the world”—takes on yet another layer of meaning. Perhaps it was not written by Thoreau the naturalist or Thoreau the poet. Perhaps instead it was written by Thoreau the tax-resister, the philosopher, the dissident.”
This is such a beautiful, artistically nourishing talk by Zach Lieberman at the 2017 AIGA Conference in Minneapolis.